Water hardness is a prevalent concern, impacting household appliances, particularly washing machines.
It is characterized by the presence of dissolved minerals, primarily calcium and magnesium, which can affect the efficiency and lifespan of appliances.
In this article we’ll go through the complexities of water hardness, its types, and its implications on washing machine performance, offering insights into mitigating its effects for sustainable laundry practices.
Table of Contents
What is water hardness?
Water hardness is a measure of the concentration of certain minerals in water, primarily calcium and magnesium. The presence of these minerals can lead to scale buildup, affecting the efficiency and longevity of household appliances like washing machines.
Water hardness is categorized into two main categories i.e., Permanent and temporary hardness.
Permanent Hardness
Permanent hardness in water is attributed to the concentration of multivalent cations, primarily calcium and magnesium ions.
These ions are notorious for their stubbornness, resisting removal through conventional methods like boiling.
Temporary Hardness
Temporary hardness is predominantly induced by dissolved bicarbonate minerals, namely calcium bicarbonate and magnesium bicarbonate.
These minerals, upon dissolution, release calcium and magnesium cations (Ca2+, Mg2+) along with carbonate and bicarbonate anions (CO2−3 and HCO−3), contributing to the water’s hardness.
The silver lining here is the “temporary” nature of this hardness.
Unlike its permanent counterpart, temporary hardness can be subdued by boiling the water or introducing lime (calcium hydroxide).
The effects of hard water on washing machines
Reduced Cleaning Performance
The presence of hard water can significantly impede the cleaning performance of washing machines.
The minerals in hard water interact with detergents, reducing their efficacy and leaving residues, which results in less vibrant and dull-looking laundry.
Increased Detergent Use
To combat the reduced efficacy, there is a notable increase in detergent use.
The minerals in hard water hinder the lather formation of detergents, necessitating the use of more products to achieve the desired cleaning results.
Shorter Lifespan of the Washing Machine
The accumulation of mineral buildup from hard water can lead to scale formation within the washing machine components, thereby reducing the appliance’s lifespan and efficiency.
Increased Risk of Breakdowns
The scale buildup not only affects the lifespan but also increases the risk of breakdowns.
The accumulation of minerals can cause blockages and impair the functioning of the washing machine, leading to more frequent maintenance and repairs.
What are the signs that you have hard water in your washing machine?
Recognizing hard water can be pivotal in maintaining optimal washing machine performance. Some indicative signs include:
- Residue on Laundry: The presence of a white, chalky residue on clothes post-washing is a telltale sign of hard water.
- Stiff Fabrics: Fabrics feeling stiff and rough post-wash can be attributed to the mineral content in hard water.
- Soil Build-up: The diminished cleaning efficacy results in soil accumulation on clothes over time.
- Faded Colors: The vibrancy of colors is compromised, with apparel appearing faded due to mineral deposits.
- Soap Scum: A noticeable buildup of soap scum in the machine or on the laundry signals potential hard water issues.
How to Reduce the Effects of Hard Water on Your Washing Machine?
Mitigating the effects of hard water on washing machines is crucial for maintaining the appliance’s performance and lifespan.
Here are some strategies to combat the challenges posed by hard water:
Use a Water Softener
Using a water softener is a proactive approach to combat hard water.
This process revolves around the elimination of calcium, magnesium, and other metal cations in hard water, thereby enhancing the water quality and reducing its hardness.
Different Types of Water Softeners and How They Work
Various water softeners are available, each employing a unique mechanism to reduce water hardness.
Ion-exchange softeners replace calcium and magnesium ions with sodium ions, while magnetic and electronic softeners alter the properties of scale-forming minerals, preventing their accumulation.
Both, types of water softeners work especially if you are dealing with temporary hardness.
Use a Detergent Specifically Designed for Hard Water
Opting for detergents formulated for hard water can enhance cleaning efficacy.
These specialized detergents are formulated especially for hard water, ensuring optimal cleaning results.
Clean Your Washing Machine Regularly
Just like any other electronic appliance or product washing machine too requires regular maintenance.
Cleaning the appliance periodically can prevent mineral buildup and scale formation, thereby preserving its functionality and efficiency.
Use a Hard Water Washing Machine
Investing in washing machines designed for hard water can be a game-changer, some notable brands that make hard water washers include Whirlpool, IFB, LG, Samsung, Haier, and Godrej.
I have not listed any specific model here because the appliance industry is constantly evolving and the models keep on getting added and discontinued.
Just read the reviews online and check e-commerce platforms like Amazon to get a washer that’s suitable for your needs.
Tips for Getting the Best Cleaning Results with Hard Water
Here are some tips to enhance your laundry experience and achieve optimal cleaning results even in the presence of hard water:
Use More Detergent
Given the interaction between hard water minerals and detergents, using a slightly higher amount of laundry detergent can help in achieving better lather formation and, consequently, improved cleaning efficacy.
Pre-treat Heavily Soiled Items
Pre-treating stains and heavily soiled items can significantly enhance the cleaning results.
Applying a stain remover or a pre-wash treatment can help break down stains and soils, making them easier to wash away during the cycle.
Also Read: What Is Prewash cycle in the washing machine?
Wash on a Longer Cycle
Opting for a longer wash cycle can provide the detergent more time to interact with the laundry, thereby improving the cleaning performance.
This can be particularly beneficial when dealing with hard water as it allows for better dissolution of detergents and thorough cleaning of fabrics.
Troubleshooting Common Washing Machine Problems Caused by Hard Water
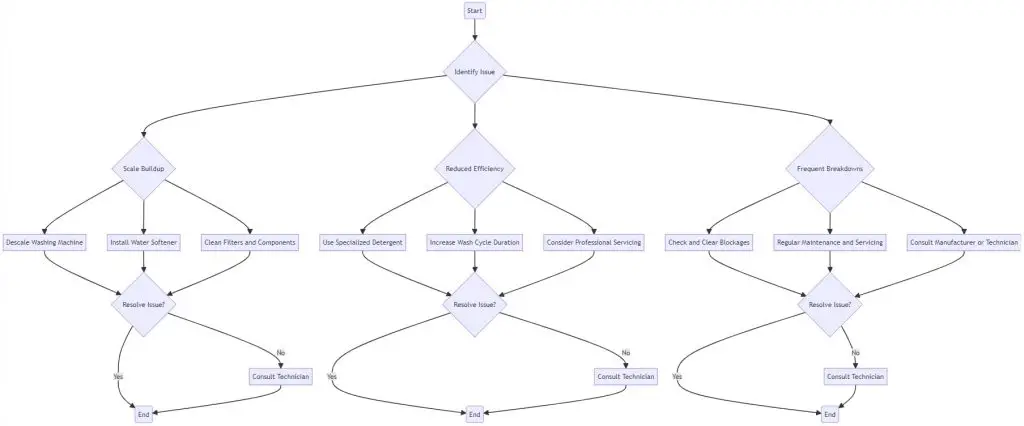
Addressing washing machine problems induced by hard water is essential for maintaining the appliance’s functionality, some common issues include:
Scale Buildup
- Issue: Scale accumulates on the heating elements and internal components.
- Solution: Run a descaling cycle using a suitable descaling agent as per the manufacturer’s instructions. Check the user manual for recommended descaling products and frequency.
Ineffective Cleaning
- Issue: Detergents are less effective due to hard water, leaving clothes unclean.
- Solution: Adjust the detergent dosage according to water hardness. Consider using a detergent formulated for hard water. Check the user manual for guidance on detergent dosage.
Staining on Clothes
- Issue: Clothes have white or gray stains due to mineral-detergent reaction.
- Solution: Use liquid detergent as it dissolves better in hard water. Run an additional rinse cycle with a water-softening agent or vinegar.
Reduced Efficiency and Increased Energy Consumption
- Issue: Scale buildup reduces machine efficiency.
- Solution: Perform regular descaling cycles. Check and clean the filter and drain pump regularly as per the user manual.
Fabric Damage and Stiffness
- Issue: Fabrics feel rough and stiff after washing.
- Solution: Use a fabric softener in the final rinse cycle. Adjust the washing machine settings as per the user manual for hard water conditions.
Blocked Jets and Pipes
- Issue: Mineral deposits block water jets and pipes.
- Solution: Inspect and clean the jets and pipes regularly. Run hot water cycles with descaling agents as recommended in the user manual.
Soap Scum Buildup
- Issue: Soap scum accumulates inside the drum and on clothes.
- Solution: Clean the drum regularly using a washing machine cleaner or a mixture of vinegar and baking soda. Refer to the user manual for cleaning instructions.
Energy Efficiency Implications of Using Hard Water in Your Washing Machine
Utilizing hard water in washing machines has notable implications on energy efficiency.
The scale and mineral buildup resulting from hard water can lead to increased energy consumption as the machine works harder to maintain its performance.
Additionally, the necessity for longer wash cycles and increased detergent use further escalates energy and resource utilization, underscoring the environmental impact of hard water.
Here’s a detailed scientific explanation of the implications:
Formation of Limescale
Hard water contains ions like calcium (Ca²⁺) and magnesium (Mg²⁺) which react with bicarbonate ions (HCO₃⁻) to form insoluble compounds such as calcium carbonate (CaCO₃) and magnesium carbonate (MgCO₃).
These compounds precipitate and form limescale on the heating elements of the washing machine.
Limescale acts as an insulator, reducing the efficiency of the heating element, which in turn requires more energy to heat water to the desired temperature.
Increased Detergent Usage
The calcium and magnesium ions in hard water react with the anionic surfactants (detergent) to form insoluble salts, reducing the effectiveness of the detergent.
The implication of this is that more detergent is required to achieve the same level of cleanliness, leading to increased chemical usage and energy consumption as the washing machine has to work harder to remove dirt and stains.
Increased Washing Time and Energy Consumption
The reduced effectiveness of detergents and the insulating effect of limescale can increase the time and energy required for washing.
The immediate side effect is that longer washing cycles and higher temperatures may be needed to achieve the same level of cleanliness, resulting in higher energy consumption and costs.
Increased Water Usage
Hard water may not rinse out as easily as soft water due to the presence of minerals.
Therefore, more water may be required for rinsing, leading to higher water consumption and energy usage for water heating and pumping.
Also Read: Portable Washer Energy Consumption: Save up to 50%
Can fully automatic washing machines wash clothes in hard water?
Using hard water in washing machines is not recommended as it requires more detergent, causes lime-scaling in machines, and results in stiffer clothes fibers.
Instead, the recommended practice is to get a washer that is capable of dealing with hard water supply or get water softeners especially if you are located in a place where there is no facility of water treatment plant.
Final Thoughts
Navigating through the challenges posed by water hardness is essential for optimizing washing machine performance and lifespan.
By using strategies such as using water softeners, specialized detergents, and regular maintenance you can mitigate the adverse effects.
Being vigilant of the signs of hard water and adopting sustainable laundry practices contribute to energy efficiency and environmental conservation, ensuring a healthy relationship between household appliances and water quality.
You May Also Like
- Powder vs Liquid Laundry Detergent For Washing Machines
- Liquid Detergent Placement in Washing Machines (Guide)
- Can Washing Machines Be Used In Freezing Weather? (Answered)
- Washing Machine Programs: A Beginner’s Guide
- Laundry Stripping for Hard Water: Revitalize Your Laundry
- Can you use regular detergent in a portable washing machine?

